Afrikaans
Conjugate VerbsFacts
- Language: Afrikaans
- Alternate names:
- Language code: afr
- Language family: Indo-European, Classical Indo-European, Germanic, Northwest Germanic, West Germanic, Macro-Dutch, Middle-Modern Dutch, Modern Dutch, Global Dutch, Afrikaansic
- Number of speakers: 5965879
- Script: Latin script
More information:
Introduction
Afrikaans is an Indo-European language, derived from Dutch, mainly spoken in South Africa and Namibia. There are smaller numbers of speakers in Botswana, Angola, Swaziland, Zimbabwe and Zambia. It was originally the dialect that developed among the Afrikaner Protestant settlers and the indentured or slave workforce brought to the Cape area in southwestern South Africa by the Dutch East India Company.
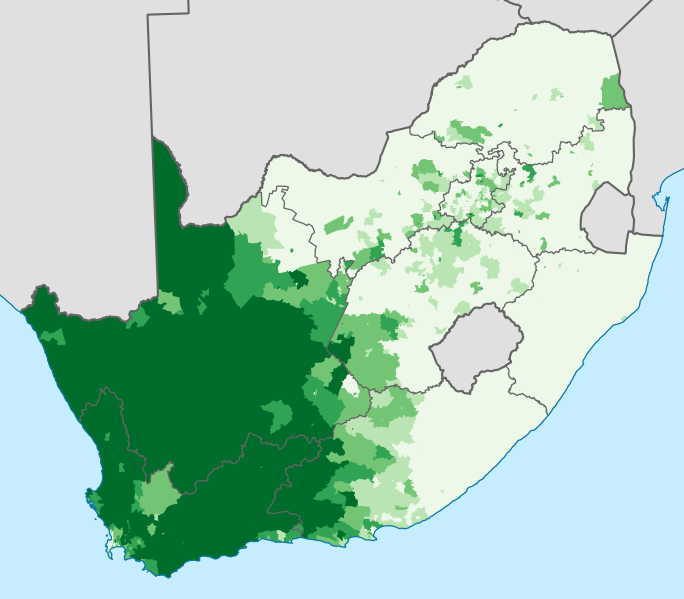
Proportion of the South African population that speaks Afrikaans as their first language, according to Census 2011 at electoral ward level. Shadows of green from lightest to darkest: -20%, 20-40%, 40-60%, 60-80%, 80%-
The verb
Apart from the ge- prefix in past participle, all verbal inflection has been lost.
Sample verb gaan 'to go'.
| Infinitive | gaan |
| Present | gaan |
| Past participle | gegaan |
The irregular verbs: wees and hê
There is no distinction between the infinitive and present forms of verbs, with the exception of wees 'to be' and hê 'to have'.
| Infinitive | wees |
| Present | is |
| Past participle | gewees |
| Infinitive | hê |
| Present | het |
| Past participle | gehad |
Verblists
References
- Donaldson, Bruce C.. A grammar of Afrikaans.
- Breyne, Marcel R.. Lehrbuch des Afrikaans. München, 1954.