Introduction
The North Germanic languages make up one of the three branches of the Germanic languages. Derived from Proto-Norse and Old Norse, they are spoken in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, the Faroe Islands, Iceland and (to some extent) Greenland, as well as by a significant Swedish minority in Finland and by immigrant groups mainly in North America and Australia.
Old Norse languages
This map shows the geographic distribution of Old Norse languages around AD900.
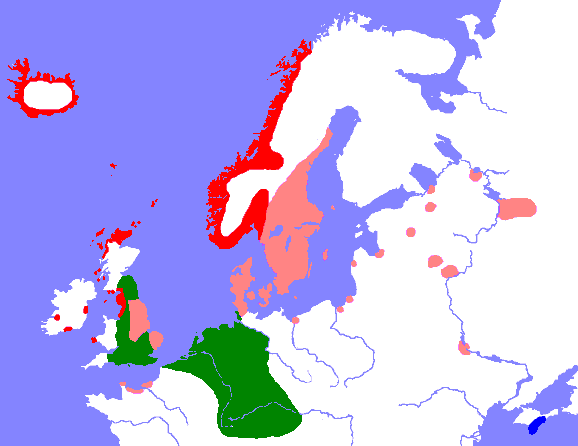
Red: Old West Norse, light-red: Old East Norse, blue: Gothic, green: other Germanic languages
Language Family Tree
Indo-European > Classical Indo-European > Germanic > Northwest Germanic > North Germanic- North Scandinavian
- East-Central Swedic
- East Swedic
- Archaic Finnish Swedish
- Estonian Swedish
- [swe] Swedish
- Early Contemporary Swedish
- Modern Gutnish
- Swedish, Aiboland
- Swedish, Degerforsmål
- Swedish, Fasternamål
- Swedish, Finland, Older
- Swedish, Gamlakarleby
- Swedish, Gammelsvenskby
- Swedish, Gotlandic
- Swedish, Härjedalen
- Swedish, Helsingfors
- Swedish, Jämtland
- Swedish, Kalix
- Swedish, Misiones
- Swedish, Närpes
- Swedish, Nyland
- Swedish, Östnyylendskå
- Swedish, Våmhus
- Dalecarlian (0 languages)
- East Swedic
- Narrow North Scandinavian
- Archaic Norrlandic
- Jamtska
- Archaic Gutnish
- East-Central Swedic
- South Scandinavian
- West Scandinavian
Languages Sorted Alphabetically
- Danish
- Danish, Sejerø
- Early Contemporary Swedish
- Early Modern Danish
- Faroese
- Icelandic
- Jutish
- Modern Gutnish
- Old Norse
- Swedish
- Swedish, Aiboland
- Swedish, Degerforsmål
- Swedish, Fasternamål
- Swedish, Finland, Older
- Swedish, Gamlakarleby
- Swedish, Gammelsvenskby
- Swedish, Gotlandic
- Swedish, Härjedalen
- Swedish, Helsingfors
- Swedish, Jämtland
- Swedish, Kalix
- Swedish, Misiones
- Swedish, Närpes
- Swedish, Nyland
- Swedish, Östnyylendskå
- Swedish, Våmhus